Woudl the Big Bang Happen Again After Heat Death
There are a number of possible cataclysms that could wipe out the human race. Have the expansion of the sun into a red giant. That'll volition somewhen absorb the Earth. This result is set to occur in about 7-8 billion years. The only manner to escape it, every bit Elon Musk and others debate, is to become an interplanetary species—if not an intergalactic one. Would such a move forever safeguard the human race?
When the universe will finish has been a topic of give-and-take amongst theoretical physicists for some time. What they can agree on is, it's probable to occur somewhere between 2.5-22 billion years from now. Nosotros'll have to find another universe to inhabit before that, if such a thing exists and if information technology's habitable to our species.
There are iii prevailing theories on how the universe will cease. 1 is the Large Crisis. This theory states that at some point, the universe will stop moving in one management and start shrinking back in on itself, perhaps condensing into the singularity once more.
Subscribe for counterintuitive, surprising, and impactful stories delivered to your inbox every Thursday
Another is the Big Rip, where the universe continues to spread out and advance at an always-increasing velocity, until it tears an enormous rend into its own fabric, spreading catastrophe everywhere. This would destroy non only stars but black holes, planets, and even whole galaxies. The universe would literally rip itself to pieces.
The last is chosen the Big Freeze. This is the "heat death" thermodynamics postulates. Until now, information technology was considered the most likely scenario. It originates with the 2d law of thermodynamics, which states that the entropy or chaos in a arrangement volition increment, until information technology overtakes the entire system.
The engine will someday seize upward for good, the human body will age and dice, and the universe volition spread out to such an extent that gases no longer congregate, significant stars will no longer course. Without birthing new stars and when all the former ones die out, the universe volition become a cold, empty, lifeless void.
Recently, a team of Harvard physicists stated that this is no longer the likeliest scenario. Instead, according to them, the cosmos is likely to terminate in another Big Bang. Merely this event will be much different than the one that birthed the cosmos. The squad's findings were published in the journal Physical Review D.
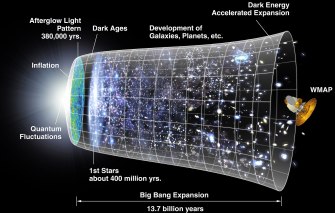
Model of the Large Bang. Credit: NASA/WMAP Science Team.
Turns out, the universe could autumn to pieces internally, depending on what occurs with the Higgs boson. Known as the "God particle," the Higgs is a miniscule quantum particle that lends other, larger particles their mass. Should the Higgs boson become destabilized, the entire universe would erupt in a massive explosion, incinerating all and everything from one end of the cosmos to the other. Then does that mean we should all get our affairs in society?
Actually, this isn't supposed to happen for another x 1000000 trillion trillion trillion trillion trillion trillion trillion trillion trillion trillion trillion years. This is of grade, only accurate if the subatomic particle's collapse hasn't already begun. If it did, we wouldn't know it. Since the Higgs field is evenly distributed throughout the universe, we would be instantly vaporized, before the event had a chance to register in our brains. Harvard scientists aren't guaranteeing it, but they're 95% certain the cosmos will finish this way.
The illusive Higgs boson was only discovered in 2012, although it has been theorized to exist every bit far dorsum every bit the 1920s. Using a Large Hadron Collider and smashing subatomic protons together, scientists were able to catch a glimpse of it. So what might cause the Higgs boson to become unstable?
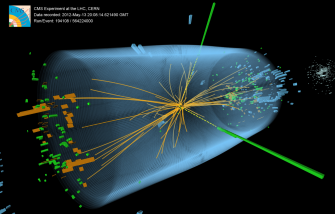
A 3D model of the detection of the Higgs boson, which occurred during a proton-proton collision in the Large Hadron Collider. Credit: CERN.
Harvard researchers conceive of a space-time curvature around a black hole, somewhere deep inside the universe. Recent astronomical observations pb united states of america to believe that a supermassive black hole sits at the eye of near every milky way, including our own. It'southward thought that clusters of other blackness holes reside near them and are eventually absorbed by them. In fact, a baker'south dozen was just discovered hanging around a supermassive black hole, nearly Sagittarius A, a densely-packed region shut to the center of our galaxy.
Since these behemothic anomalies don't operate according to the laws of standard physics, ablack hole could theoretically change the Higgs boson'southward mass, destabilizing the field. Physicist Joseph Lykken and the late Stephen Hawking were the first to propose the collapse of the Higgs boson field as a potential doomsday scenario. "It turns out nosotros're right on the border between a stable universe and an unstable universe," Lykken told the New York Post. "We're sort of right on the border where the universe tin last for a long time, but eventually, it should get 'nail.'"
To larn more virtually the Higgs boson, click here.
Source: https://bigthink.com/surprising-science/a-second-big-bang-will-likely-destroy-the-universe-harvard-researchers-say/
0 Response to "Woudl the Big Bang Happen Again After Heat Death"
Post a Comment